Wild And Domestic Animals
wild and domestic animals by Delta publications

key notes:
Definition:
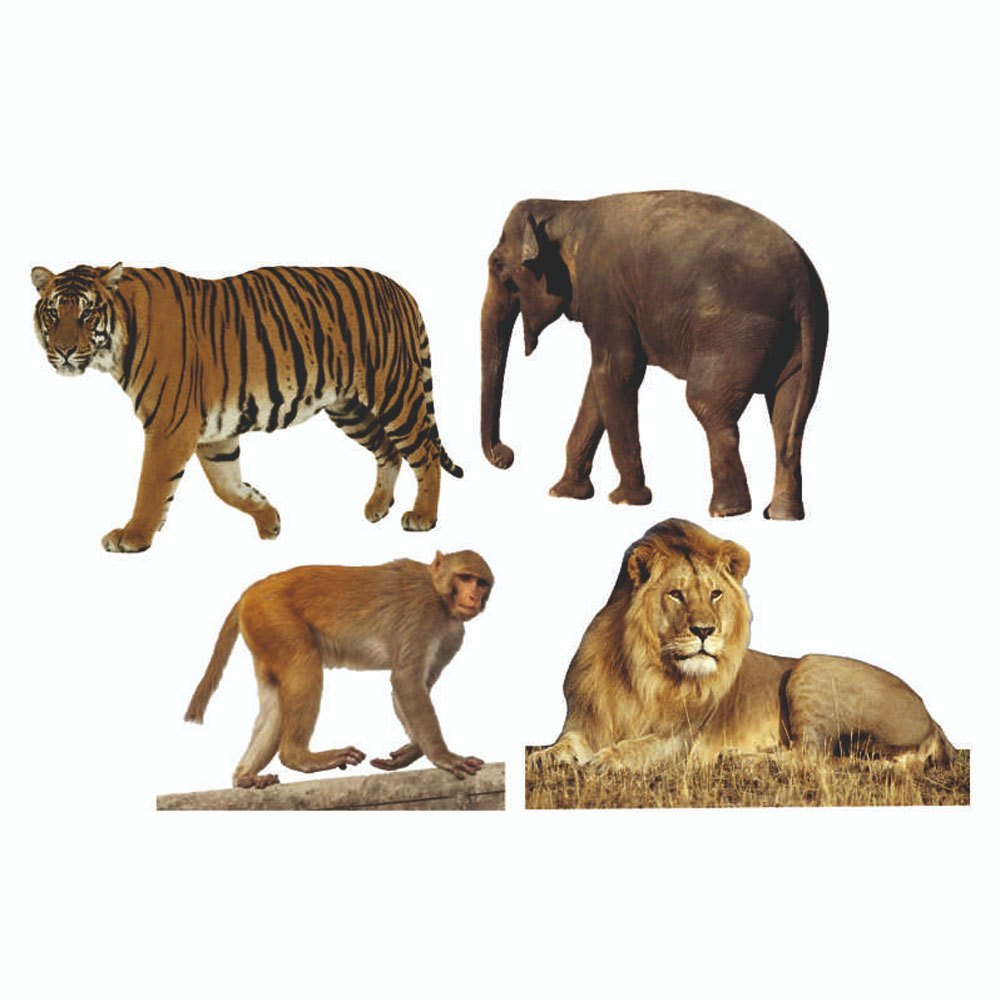
- Wild Animals: Animals that live in natural habitats like forests, jungles, or deserts and are not dependent on humans for food or shelter.

- Domestic Animals: Animals that live near or with humans and depend on them for food, shelter, and care.
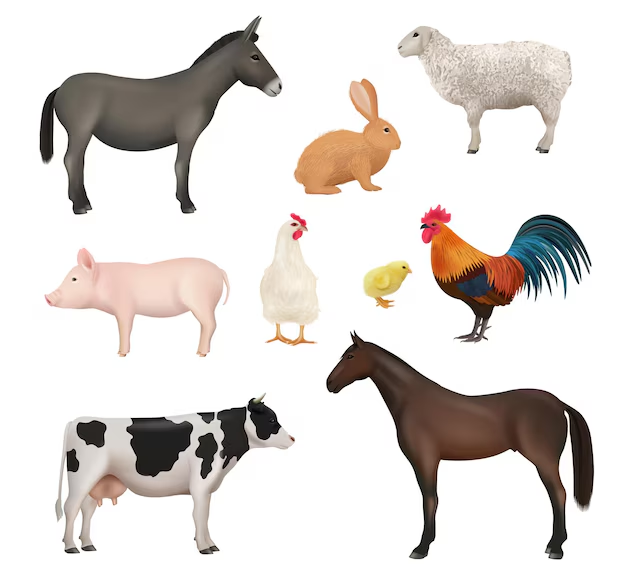
Examples:
- Wild Animals: Lion, tiger, elephant, giraffe, zebra, bear, etc.

- Domestic Animals: Dog, cat, cow, goat, horse, sheep, etc.

Habitat:
- Wild animals live in places like forests, mountains, and rivers.
- Domestic animals live on farms or in homes.
Purpose:
- Wild animals maintain the balance of nature.
- Domestic animals help humans in various ways, like providing milk, meat, or wool and being companions.
Characteristics:
- Wild animals are self-sufficient and usually have to hunt or forage for food.
- Domestic animals are trained or tamed and often friendly towards humans.
Care for Domestic Animals:

- Provide proper food and clean water.
- Give them shelter and take them to a vet when they are sick.
Wild Animals Safety:

- Observe them from a safe distance in zoos or wildlife sanctuaries.
- Never approach or try to feed wild animals.
Importance of Both:
- Wild animals are important for biodiversity.
- Domestic animals are important for human life and livelihood.
Interesting Fact:
- Some animals can be both wild and domestic, like elephants, which are tamed in some regions but live freely in others.
Let’s practice!🖊️

